廬山東林寺三笑庭名聯‧清‧唐蝸寄
橋跨虎溪,三教三源流,三人三笑語;
蓮開僧舍,一花一世界,一葉一如來。
曾經三人三笑語,聞得虎嘯,恍然大悟。何故三詠三抒懷︰
詠二疏‧陶淵明
大象轉四時,功成者自去。
借問衰周來,幾人得其趣?
遊目漢廷中,二疏復此舉。
高嘯返舊居,長揖儲君傅。
餞送傾皇朝,華軒盈道路。
離別情所悲,余榮何足顧!
事勝感行人,賢哉豈常譽?
厭厭閭裏歡,所營非近務。
促席延故老,揮觴道平素。
問金終寄心,清言曉未悟。
放意樂餘年,遑恤身後慮。
誰雲其人亡,久而道彌著。
詠三良‧陶淵明
彈冠乘通津,但懼時我遺;
服勤盡歲月,常恐功愈微。
忠情謬獲露,遂為君所私。
出則陪文輿,入必侍丹帷;
箴規向已從,計議初無虧。
一朝長逝後,願言同此歸。
厚恩因難忘,君命安可違?
臨穴罔惟疑,投義誌攸希。
荊棘籠高墳,黃鳥聲正悲。
良人不可贖,泫然沾我衣。
詠荊軻‧陶淵明
燕丹善養士,誌在報強嬴。
招集百夫良,歲暮得荊卿。
君子死知己,提劍出燕京;
素驥鳴廣陌,慷慨送我行。
雄發指危冠,猛氣衝長纓。
飲餞易水上,四座列群英。
漸離擊悲筑,宋意唱高聲。
蕭蕭哀風逝,淡淡寒波生。
商音更流涕,羽奏壯士驚。
心知去不歸,且有後世名。
登車何時顧,飛蓋入秦庭。
淩厲越萬裏,逶迤過千城。
圖窮事自至,豪主正怔營。
惜哉劍術疏,奇功遂不成!
其人雖已沒,千載有餘情。
晉時淵明,晉後名潛,已棄五斗米,不知姓字忘其何人,五柳先生『伍』『柳』吟誦耶??果真二三子其志一也!!雖說是移時隔空得失不同,其人其心何其相似乎??!!先生『菀柳』之『情』仍一樣吧!!??
誰雲其人亡,久而道彌著。
良人不可贖,泫然沾我衣。
其人雖已沒,千載有餘情。
大暑已過,入秋之際,講此『春耕夏耘』之『心法』勒。古今中外『學問』縱有千百種,談起功夫『心法』則一矣。往往其『志一』其『人同』也!!只是『一花』『一葉』真誠對待歟??
─── 《光的世界︰派生科學計算六‧下》
字裡行間逐詞意,詞意或解概念難!
聲韻音節是何物?
Syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds. For example, the word water is composed of two syllables: wa and ter. A syllable is typically made up of a syllable nucleus (most often a vowel) with optional initial and final margins (typically, consonants).
Syllables are often considered the phonological “building blocks” of words. They can influence the rhythm of a language, its prosody, its poetic meter and its stress patterns.
Syllabic writing began several hundred years before the first letters. The earliest recorded syllables are on tablets written around 2800 BC in the Sumerian city of Ur. This shift from pictograms to syllables has been called “the most important advance in the history of writing“.[1]
A word that consists of a single syllable (like English dog) is called a monosyllable (and is said to be monosyllabic). Similar terms include disyllable (and disyllabic; also bisyllable and bisyllabic) for a word of two syllables; trisyllable (and trisyllabic) for a word of three syllables; and polysyllable (and polysyllabic), which may refer either to a word of more than three syllables or to any word of more than one syllable.
初聲始發自心田!?
Onset (audio)
Onset refers to the beginning of a musical note or other sound. It is related to (but different from) the concept of a transient: all musical notes have an onset, but do not necessarily include an initial transient.
In phonetics the term is used differently – see syllable onset.
Onset detection
In signal processing, onset detection is an active research area. For example, the MIREX annual competition features an Audio Onset Detection contest.
Approaches to onset detection can operate in the time domain, frequency domain, phase domain, or complex domain, and include looking for:
- Increases in spectral energy
- Changes in spectral energy distribution (spectral flux) or phase
- Changes in detected pitch – e.g. using a polyphonic pitch detection algorithm
- Spectral patterns recognisable by machine learning techniques such as neural networks.
Simpler techniques such as detecting increases in time-domain amplitude can typically lead to an unsatisfactorily high amount of false positives or false negatives.
The aim is often to judge onsets similarly to how a human would: so psychoacoustically-motivated strategies may be employed. Sometimes the onset detector can be restricted to a particular domain (depending on intended application), for example being targeted at detecting percussive onsets. With a narrower focus, it can be more straightforward to obtain reliable detection.
轉身反取坎離劍
Onset detection
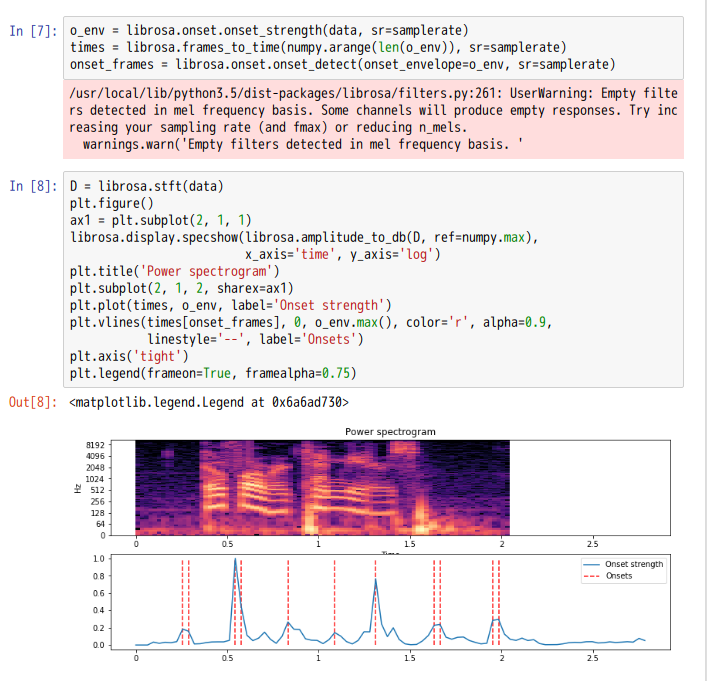
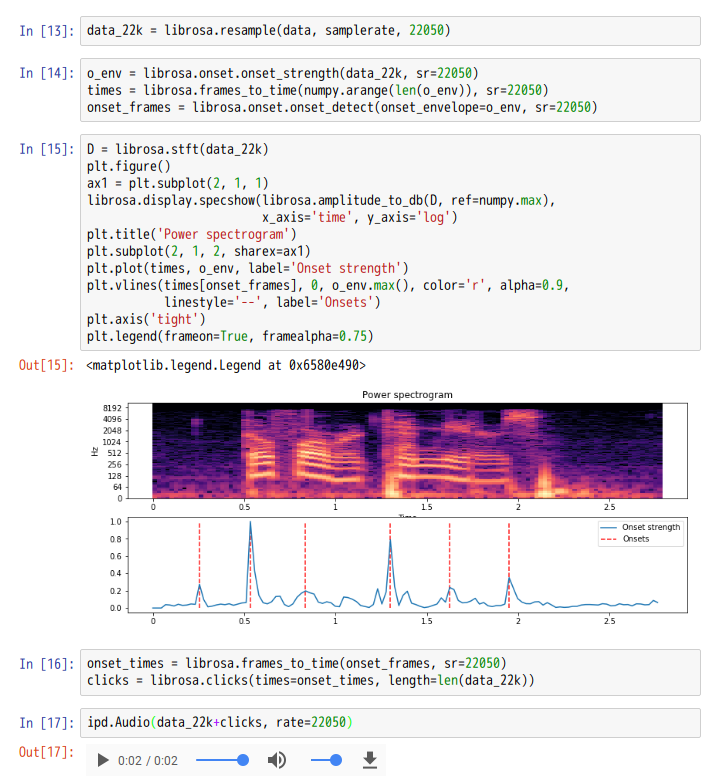
onset_detect([y, sr, onset_envelope, …]) |
Basic onset detector. |
onset_backtrack(events, energy) |
Backtrack detected onset events to the nearest preceding local minimum of an energy function. |
onset_strength([y, sr, S, lag, max_size, …]) |
Compute a spectral flux onset strength envelope. |
onset_strength_multi([y, sr, S, lag, …]) |
Compute a spectral flux onset strength envelope across multiple channels. |
耳聰目明珠璣傳◎

※ 參讀
‧ 《【鼎革‧革鼎】︰ Raspbian Stretch 《六之 J.3‧MIR-13.2 》》
‧ 《【鼎革‧革鼎】︰ Raspbian Stretch 《六之 J.3‧MIR-13.6 》》