反思此刻距離 W. David Wright 和 John Guild 作『色彩匹配』實驗也差不多百年哩!從今天觀過去,彷彿由未來看現在乎?一時出神,憶起了『三光眼鏡』︰
不知何時 Mrphs 遞給了我一副眼鏡,說道︰這是小學堂『教具室』研發的『三光眼鏡』,可以觀看而且調變『可見光』、『紅外線』 、『紫外線』的影像顯示。直須戴上就好,和貴處普通眼鏡一般。戴上後,向著『幽竟夢卿』望去,當真是目瞪口呆。只見
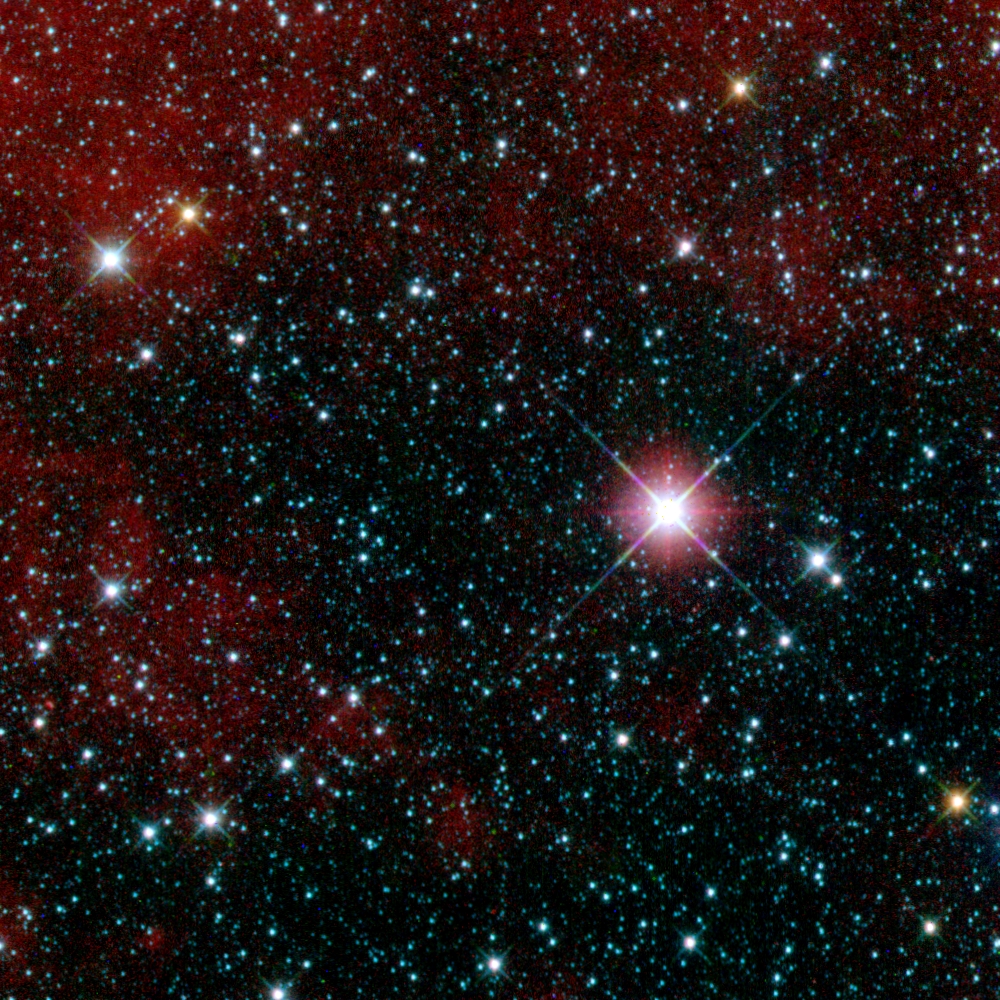
星空綺麗
This infrared space telescope image has (false color) blue, green and red corresponding to 3.4, 4.6, and 12 µm wavelengths, respectively.
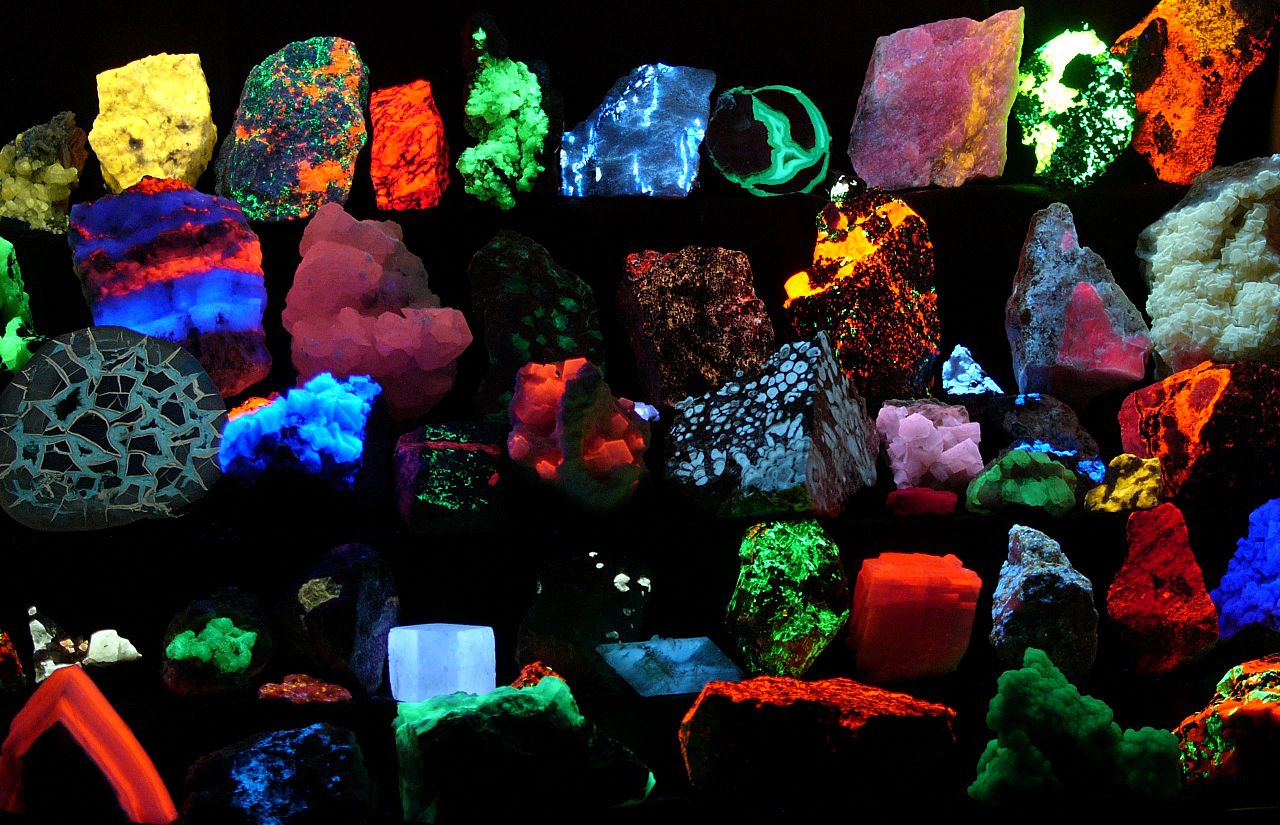
砂石熒熒
A collection of mineral samples brilliantly fluorescing at various wavelengths as seen while being irradiated by UV light.
草木含情。
心思這個世界在不同的光照下竟會是那麼的奇特美麗。心想為何要叫做『三光』的呢?『教具室』是何處的耶??剛打算開口問,就聽 Mrphs 講︰『三光』之名來自《三字經》的
意在研究『日月星』的『光譜』與『生命』之關係。當地人都知道這個『教具室』雖只致力研發『教具』與『教材』,事實上卻是《卡夫卡村》尖端之科技的代表,推動『科學教育』目標之實踐。努力『科技護生』宗旨之完成。因此才催促先生快點前行的哩。
─── 摘自《勇闖新世界︰ W!o《卡夫卡村》變形祭︰感知自然‧幽夢‧四》
喃喃自語說︰莫非那是『光譜原色』顯示器耶!!『紫外線』、『紅外線』難到可以眼見的嗎??
茫茫渺渺之際,似乎有人耳邊輕聲道︰光譜無盡廣,知覺通道多。人因經驗故,色彩擬二維,光度司明暗。黑白立兩極,五數定其原 。生生無窮意,感受實不同 。三光借假色,溝通眾有情,覺數互譯轉,無礙…… 突回神轉頭尋講話者誰,卻已無聲無影也。
一時心惆悵,轉念『記音之字』非『記義』,不細推敲寫下,恐怕失之毫釐謬以千里啊。
思之再三後,此段文字講『色彩空間』算法呀!若問人們感知的『顏色』 ![]() 為何能分成『色彩』與『明度』呢?因為人們覺得
為何能分成『色彩』與『明度』呢?因為人們覺得 ![]() 與
與 ![]() 只不過是『不同明度』之『同色彩』也。故而可用
只不過是『不同明度』之『同色彩』也。故而可用
![]()
表示『色彩』,『明度』另計哩。所以說︰『色彩擬二維,光度司明暗』。『黑色』『無明』、『白色』『大明』因此『立兩極』,輔之以『 LMS 三視錐說』,『紅、綠、藍、黑、白』『五個覺數』就決定了人之『色彩空間』矣☆
LMS color space
LMS is a color space represented by the response of the three types of cones of the human eye, named after their responsivity (sensitivity) at long, medium and short wavelengths.
It is common to use the LMS color space when performing chromatic adaptation (estimating the appearance of a sample under a different illuminant). It’s also useful in the study of color blindness, when one or more cone types are defective.
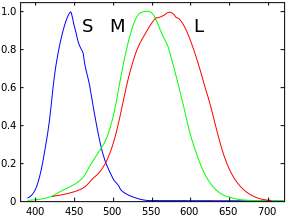
Normalized responsivity spectra of human cone cells, S, M, and L types
XYZ to LMS
Typically, colors to be adapted chromatically will be specified in a color space other than LMS. The chromatic adaptation matrix in the von Kries transform method, however, expects the LMS color space. Since colors in any color space can, by definition, be transformed to the XYZ color space, only one additional transformation matrix is required to transform colors from the XYZ color space to the LMS color space.
Since the LMS color space is supposed to model the complex human color perception, no single, “objective” transformation matrix between XYZ and LMS exists[ref ?]. Instead, various Color Appearance Models (CAMs) offer various Chromatic Adaptation Transform (CAT) matrices M as part of their modeling of human color perception.
The CAT matrices for some CAMs in terms of CIEXYZ coordinates are presented here.
- Notes
- All tristimulus values are normally calculated using the CIE 1931 2° standard colorimetric observer.[1]
- Unless specified otherwise, the CAT matrices are normalized (the elements in a row add up to unity) so the tristimulus values for an equal-energy illuminant (X=Y=Z), like CIE Illuminant E, produce equal LMS values.[1]
Hunt, RLAB
The Hunt and RLAB color appearance models use the Hunt-Pointer-Estevez transformation matrix (MHPE) for conversion from CIE XYZ to LMS.[1][2] This is the transformation matrix which was originally used in conjunction with the von Kries transform method, and is therefore also called von Kries transformation matrix (MvonKries).
| Equal-energy illuminants: |  |
| Normalized to D65: |  |
CIECAM97s, LLAB
The original CIECAM97s color appearance model uses the Bradford transformation matrix (MBFD) (as does the LLAB color appearance model).[1] This is a “spectrally sharpened” transformation matrix (i.e. the L and M cone response curves are narrower and more distinct from each other). The Bradford transformation matrix was supposed to work in conjunction with a modified von Kries transform method which introduced a small non-linearity in the S (blue) channel. However, outside of CIECAM97s and LLAB this is often neglected and the Bradford transformation matrix is used in conjunction with the linear von Kries transform method, explicitly so in ICC profiles.[3]
A revised version of CIECAM97s switches back to a linear transform method and introduces a corresponding transformation matrix (MCAT97s):[4]




