閱讀 Justin Peatross 和 Michael Ware 先生們寫的書是種享受,不急不徐娓娓道來,短短篇章竟能將『光』從馬克士威電磁波方程式
![]() ,
,
帶到『波前』 ![]() 之『圖像』 eikonal 方程式
之『圖像』 eikonal 方程式
![]() 。
。
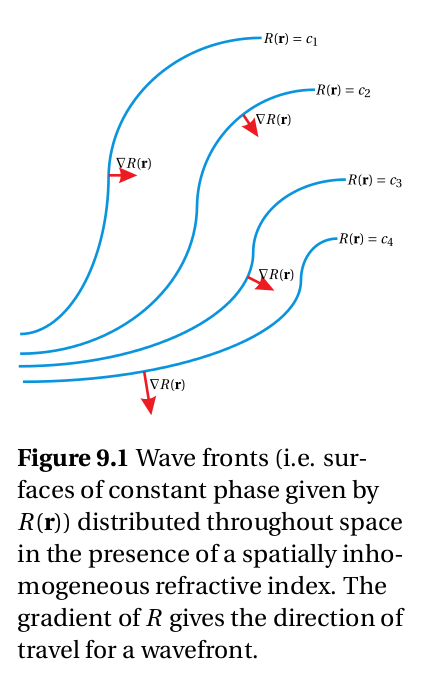
不僅解釋了德文『eikonal』命名之歷史淵源,還用摩登字『icon』描述它與『成像』的本根聯繫!!這個 ![]() 變化最快之方向,是『波前』的梯度場,也就是『能量流』之方向也︰
變化最快之方向,是『波前』的梯度場,也就是『能量流』之方向也︰
坡印廷向量
坡印廷向量(英語:Poynting vector),亦稱能流密度向量,其方向為電磁能傳遞方向,大小為能流密度(單位面積的能量傳輸速率 )。坡印廷向量的SI單位是瓦特每平方米(W/m2)。它是以其發現者約翰·坡印廷(John Henry Poynting)來命名。奧利弗·黑維塞[1]和尼科萊·烏諾夫[2]:147亦獨立發現所謂的坡印廷向量。
Poynting vector
In physics, the Poynting vector represents the directional energy flux density (the rate of energy transfer per unit area) of an electromagnetic field. The SI unit of the Poynting vector is the watt per square metre (W/m2). It is named after its discoverer John Henry Poynting who first derived it in 1884.[1]:132 Oliver Heaviside[1]:132 and Nikolay Umov[2]:147 also independently discovered the Poynting vector.
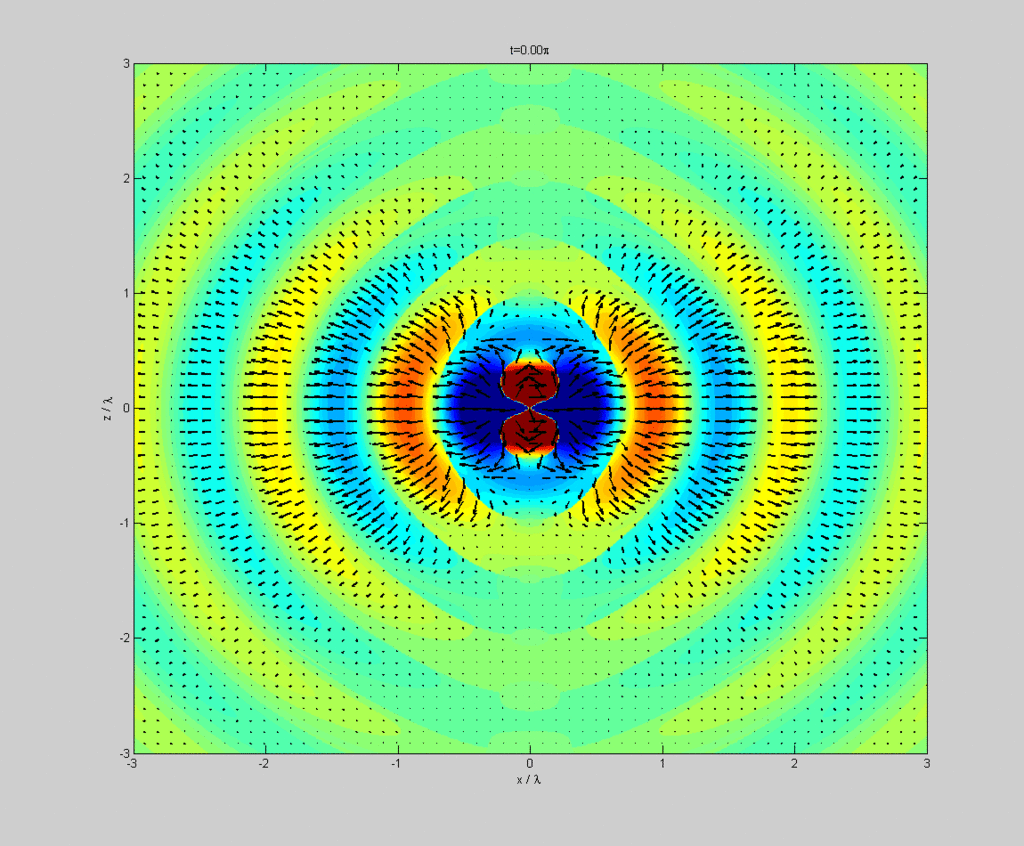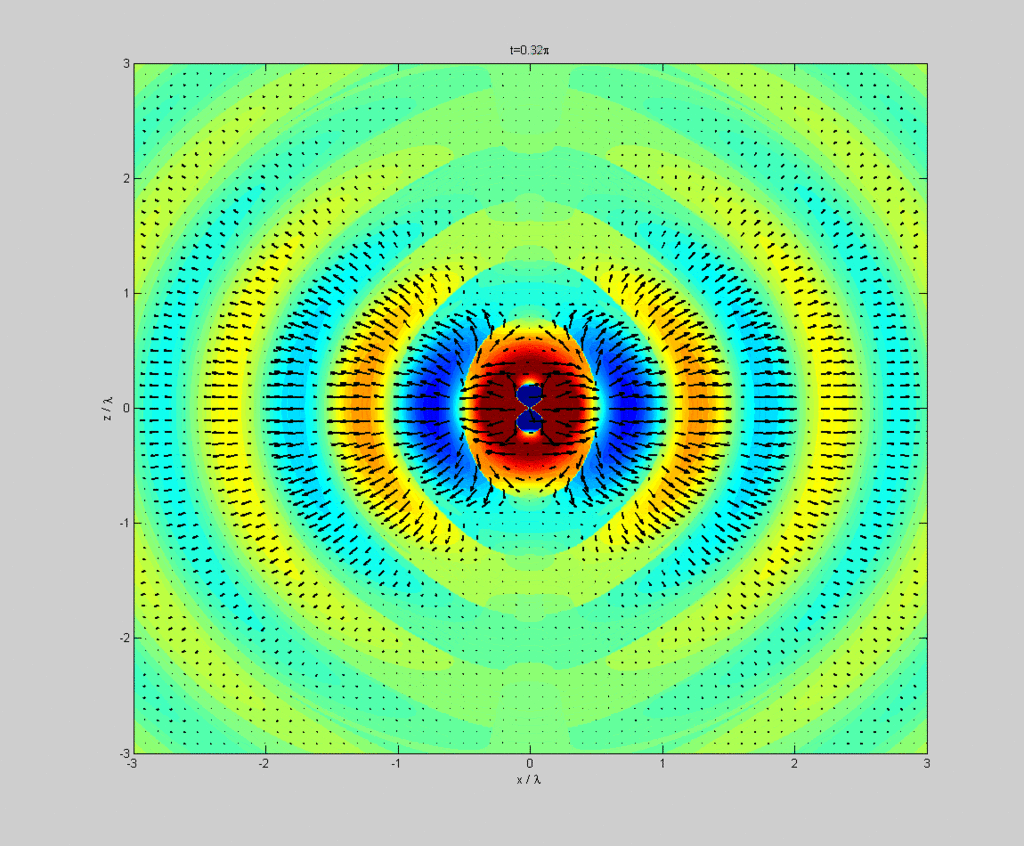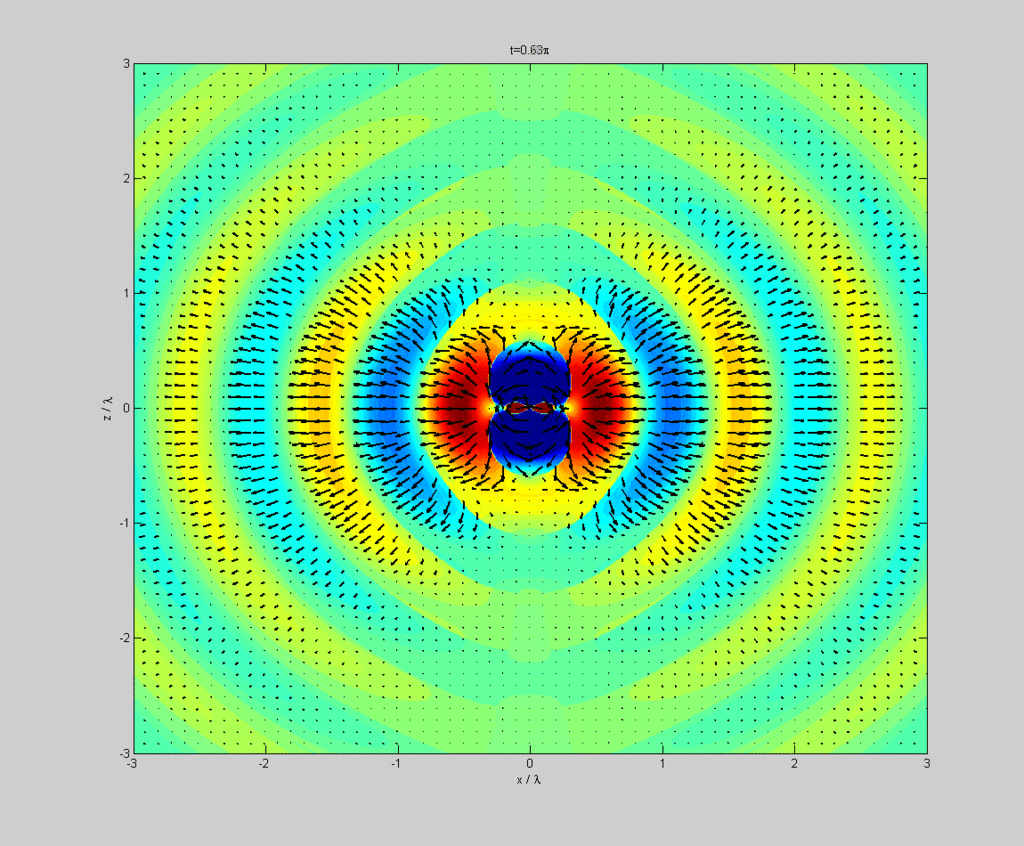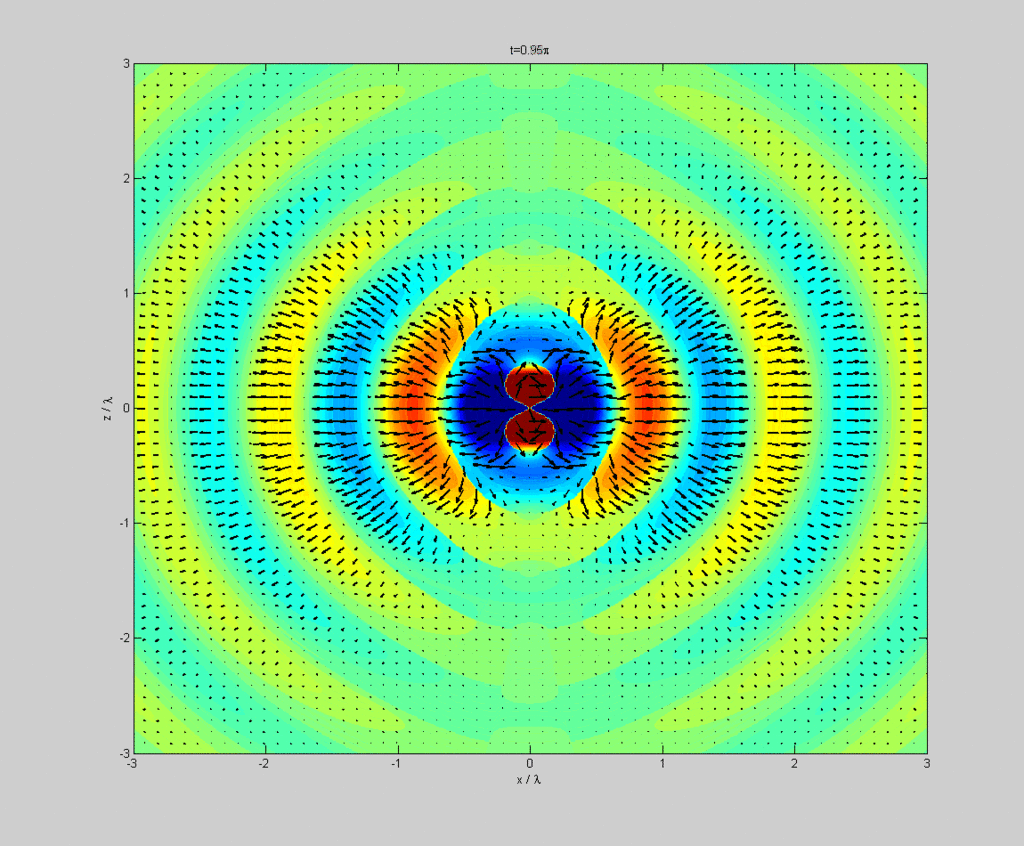
Dipole radiation of a dipole vertically in the page showing electric field strength (colour) and Poynting vector (arrows) in the plane of the page.
直 想叫『光線』現形的乎??!!

更別講此書所舉許多的 『範例』都極具『啟發性』,此處且拿這章第一例『海市蜃樓』︰
宋朝沈括在《夢溪筆談》中這樣寫道:「登州海中,時有雲氣,如宮室、臺觀、城堞、人物、車馬、冠蓋,歷歷可見,謂之『海市』 。或曰『蛟蜃之氣所為』[7],疑不然也。歐陽文忠曾出使河朔,過高唐縣,驛捨中夜有鬼神自空中過,車馬人畜之聲一一可辨,其說甚詳,此不具紀。問本處父老,云:『二十年前嘗晝過縣,亦歷歷見人物。』土人亦謂之『海市』,與登州所見大略相類也。」
來說︰

『範例』之『答案』寫在右,『圖示』畫在左︰
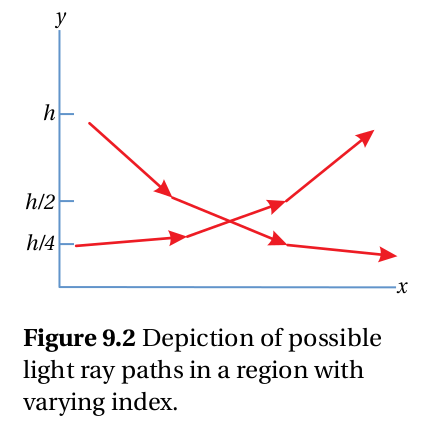
隻字未提『為何如此』哩!!??應是希望學習者『自己思考』,方能融會貫通的吧!!!否則何必婉拒『題解』乎???
Optics Textbook
Physics of Light and Optics is a high-quality free textbook desiged for an advanced undergraduate optics course for physics majors. It is used at universities around the world. You are welcome to use the text for your course or personal study or for a formal course within the following guidelines:
- The text may not be sold for profit. If you would like to use it in a class, you may provide copies to the students for the cost of printing.
- Please do not publish solutions to the homework problems.
- Please let us know if you use the text for either personal or classroom study; we would like to know how widely the book is used!
The textbook is available in PDF format on this web site, and also as a printed and bound copy available for the cost of printing, available here:
The authors (Justin Peatross and Michael Ware) welcome constructive feedback, which can be sent to opticsbook@byu.edu.
作者自然入境問俗矣☆
卒哭乃諱。禮,不諱嫌名。二名不偏諱。逮事父母,則諱王父母;不逮事父母,則不諱王父母。君所無私諱,大夫之所有公諱。詩書不諱,臨文不諱,廟中不諱。夫人之諱,雖質君之前,臣不諱也,婦諱不出門。大功小功不諱。入竟而問禁,入國而問俗,入門而問諱。
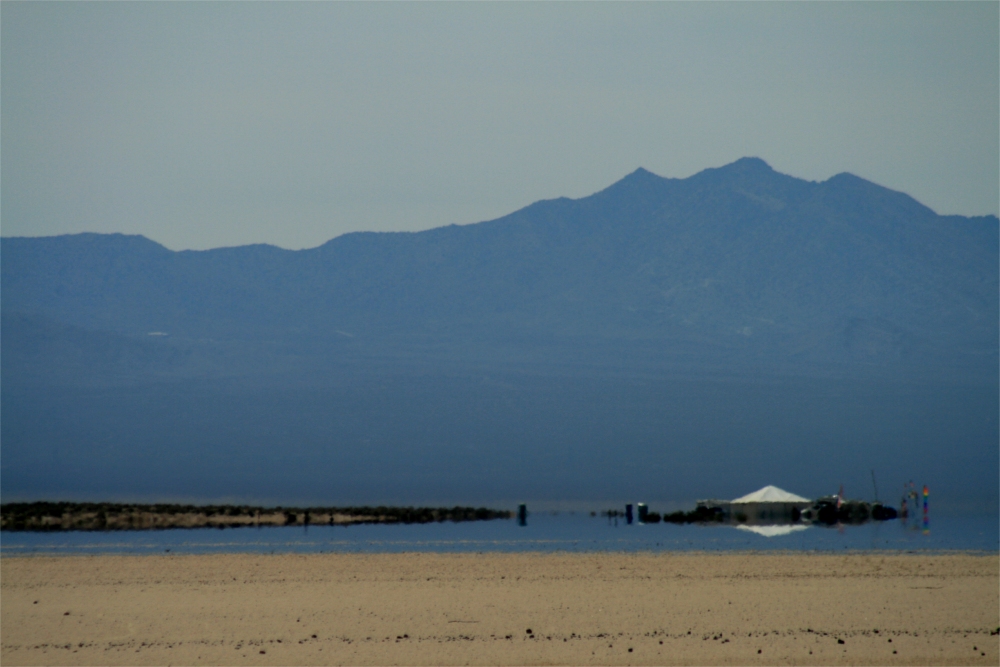

An inferior mirage on the Mojave Desert in spring
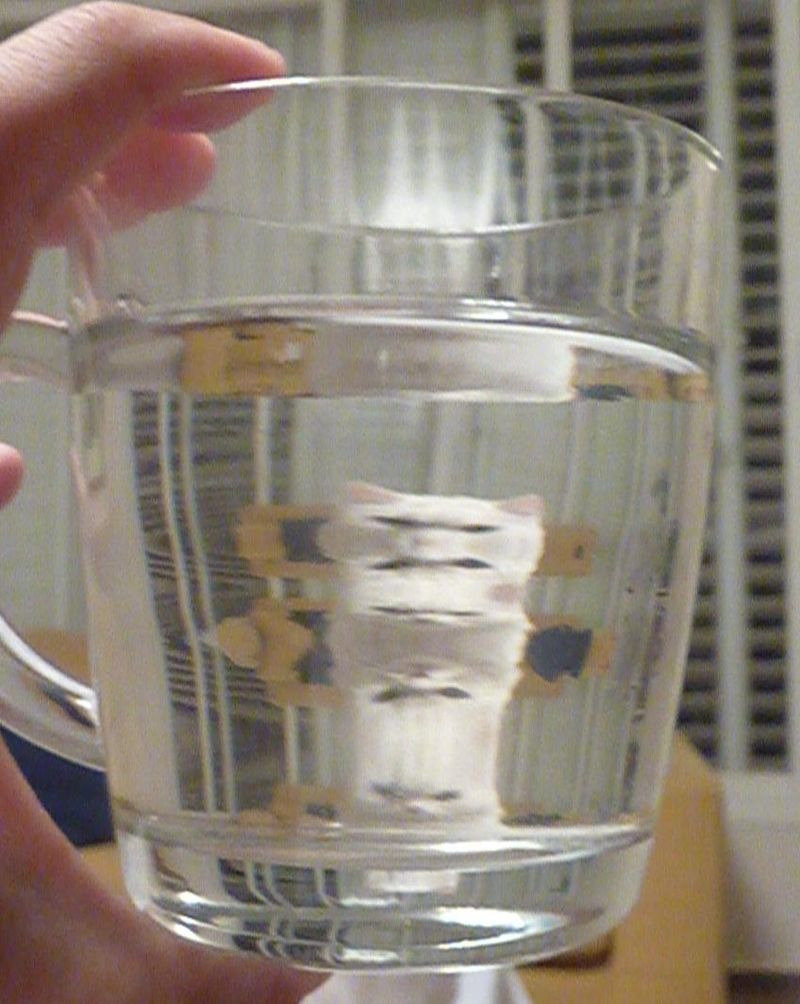

An artificial mirage, using sugar solutions to simulate the inversion layers. A cat is seen looking through a glass, which has three layers of solution, with decreasing refractive index from bottom to top. The cat appears in multiple images. This simulates an atmosphere with two inversion layers.
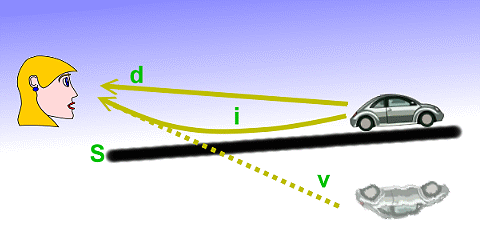
大氣的折射造成海市蜃樓
成因
冷空氣的密度比暖空氣大,因此有較大的折射率。當光線由冷空氣進入有著明確邊界的暖空氣,光線會彎曲偏離溫度梯度的方向;當光線由暖空氣進入冷空氣,它們會偏向接近梯度的方向。如果接近地面的空氣比更上面的溫暖,光線會彎曲成朝上呈現凹線的軌跡。
一旦光線抵達觀測者的眼睛,視覺皮層將解釋成它是沿著「視線」筆直的前進,然而這條線只是它抵達人眼處弧線的切線方向。結果是天空上的下蜃景似乎是在地面上。觀測者可能會錯誤的解釋這些景象是水反射至空中的,對大腦而言,這是較為合理和常發生的。
在地面的空氣比上層微冷的狀況,光線會被偏折朝下,產生「上蜃景」。
「寧靜」狀態的地球大氣層垂直梯度大約是高度每升高100米,溫度變化-1℃ (數值是負的是因為溫度隨高度增加而降低)。發生蜃景的溫度梯度必須比這個大許多。依據M. Minnaert[2],這個溫度梯度的量級至少是每米2℃,而要達到每米4℃或5℃才會出現明顯的蜃景。這些條件常出現在被強力加熱的地面,例如,當太陽一直照耀著砂或瀝青,通常就會生成下蜃景的景象。
