如果說人們建造大型強子對撞機
Large Hadron Collider
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world’s largest and most powerful particle collider, the largest, most complex experimental facility ever built, and the largest single machine in the world.[1] It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and engineers from over 100 countries, as well as hundreds of universities and laboratories.[2] It lies in a tunnel 27 kilometres (17 mi) in circumference, as deep as 175 metres (574 ft) beneath the France–Switzerland border near Geneva, Switzerland. Its first research run took place from 30 March 2010 to 13 February 2013 at an initial energy of 3.5 teraelectronvolts (TeV) per beam (7 TeV total), almost 4 times more than the previous world record for a collider,[3] rising to 4 TeV per beam (8 TeV total) from 2012.[4][5] On 13 February 2013 the LHC’s first run officially ended, and it was shut down for planned upgrades. ‘Test’ collisions restarted in the upgraded collider on 5 April 2015,[6][7] reaching 6.5 TeV per beam on 20 May 2015 (13 TeV total, the current world record). Its second research run commenced on schedule, on 3 June 2015.[8]
The LHC’s aim is to allow physicists to test the predictions of different theories of particle physics, high-energy physics and in particular, to further test the properties of the Higgs boson[9] and the large family of new particles predicted by supersymmetric theories,[10] and other unsolved questions of physics, advancing human understanding of physical laws. It contains seven detectors, each designed for certain kinds of research. The proton-proton collision is the primary operation method, but the LHC has also collided protons with lead nuclei for two months in 2013 and used lead–lead collisions for about one month each in 2010, 2011, 2013 and 2015 for other investigations.
The LHC’s computing grid is a world record holder. Data from collisions was produced at an unprecedented rate for the time of first collisions, tens of petabytes per year, a major challenge at the time, to be analysed by a grid-based computer network infrastructure connecting 140 computing centres in 35 countries[11][12] – by 2012 the Worldwide LHC Computing Grid was also the world’s largest distributed computing grid, comprising over 170 computing facilities in a worldwide network across 36 countries.[13][14][15]
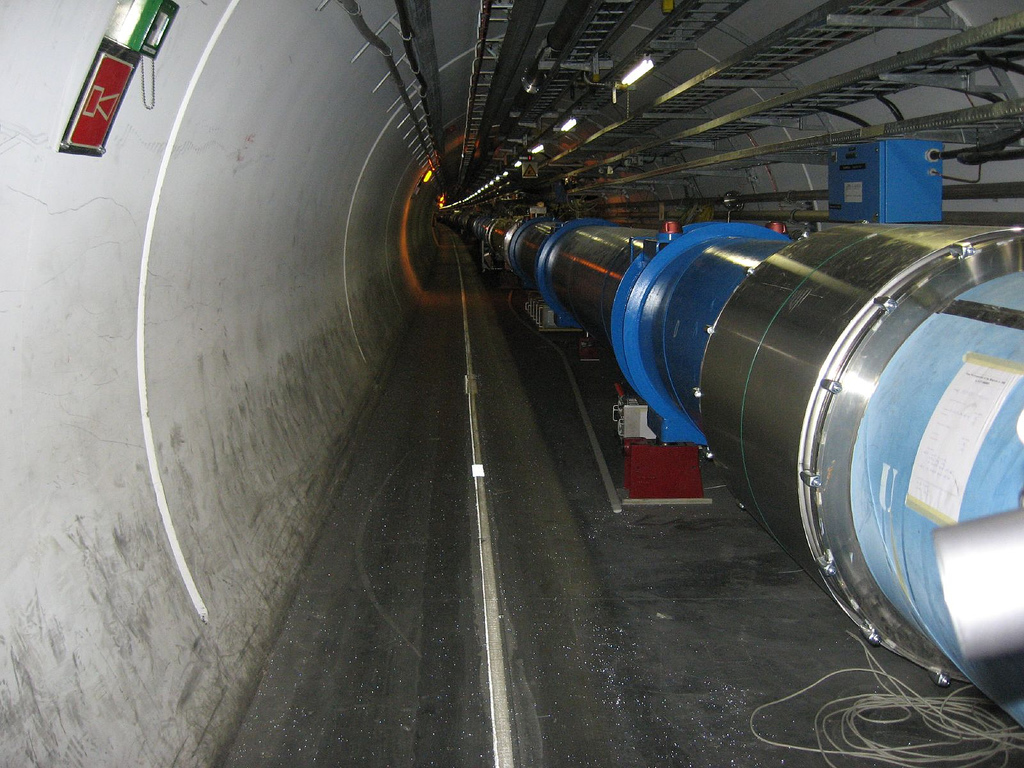

A section of the LHC
是為了探索宇宙未知的奧秘。
那麼創作超級對撞機
SuperCollider
SuperCollider 是一個最初由 James McCartney 在1996年發布的程式語言和聲音編程環境,主要用於實時聲音合成和算法作曲。[1][2]
自此之後,它逐步變成一個被科學家與藝術家們共同開發和操作聲音的系統。這個高效和有表現力的動態語言,為聲學、 算法音樂和交互式編程提供了一個框架。[3]
在2002年以GNU通用公共許可協議發布,SuperCollider 是自由軟體。 最新的主發行版(3.6.6)在2013年11月發布。[4]
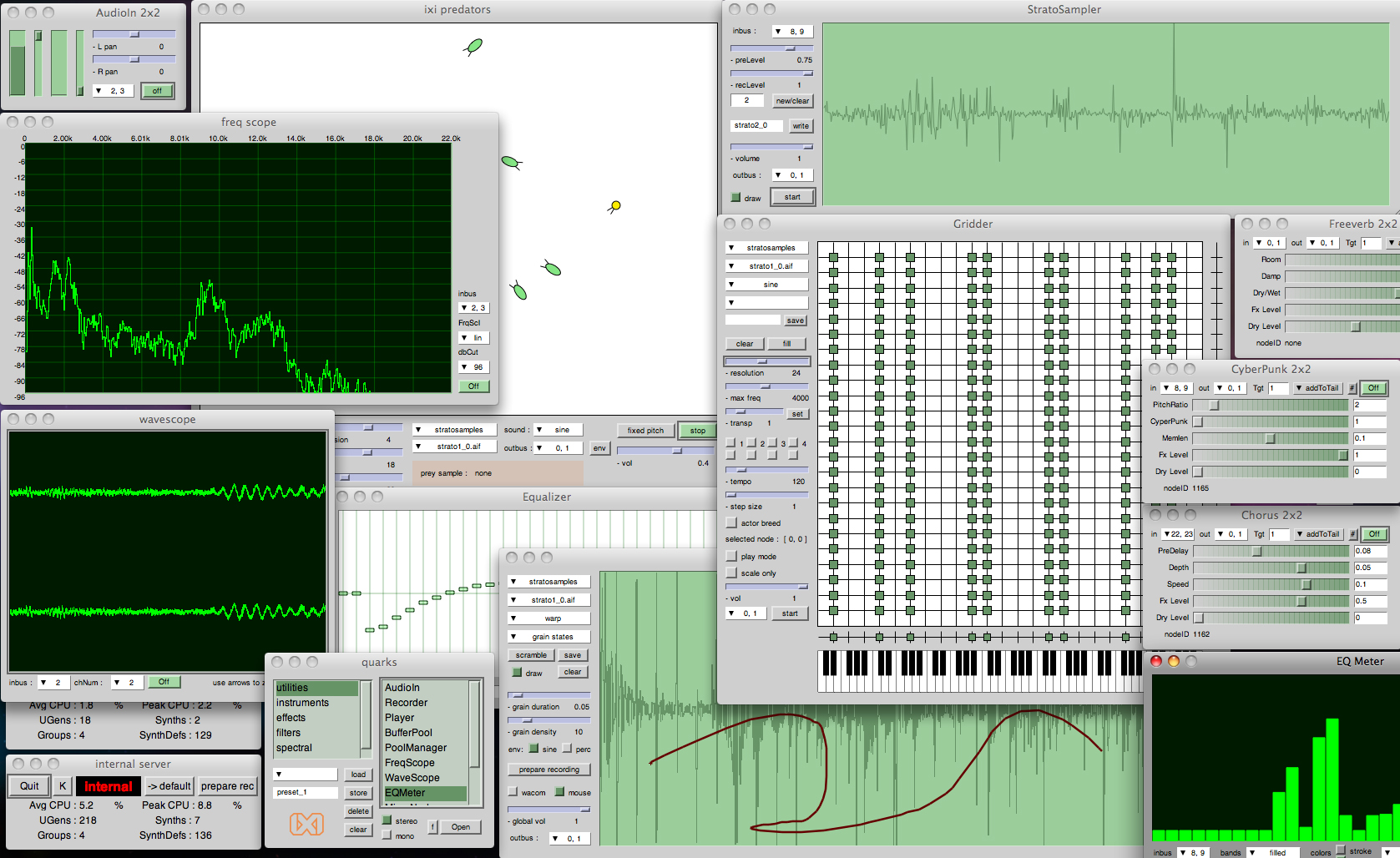
Screenshot of SuperCollider running the ixiQuarks GUI tools.
之實時聲音合成 scsynth 、程式語言 sclang 和聲音編程環境 scide︰
SuperCollider is a platform for audio synthesis and algorithmic composition, used by musicians, artists, and researchers working with sound. It is free and open source software available for Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux.
SuperCollider features three major components:
- scsynth, a real-time audio server, forms the core of the platform. It features 400+ unit generators (“UGens”) for analysis, synthesis, and processing. Some of the audio techniques it supports include additive synthesis, subtractive, FM, granular, FFT, and physical modelling. You can write your own UGens in C++, and users have already contributed several hundred more to the sc3-plugins repository.
- sclang, an interpreted programming language, controls scsynth via Open Sound Control. You can use sclang for algorithmic sequencing, connecting your app to external hardware including MIDI controllers, or writing GUIs and visual displays. sclang has a stock of user-contributed extensions called Quarks.
- scide is an editor for sclang with an integrated help system.
SuperCollider was developed by James McCartney and originally released in 1996. In 2002, he generously released it as free software under the GNU General Public License. It is now maintained and developed by an active and enthusiastic community.
是尋找聲子的蹤跡?窮究有聲世界之起源乎!
聲子共和國之理念是音聲共鳴和奏,有聲能與有情水乳交融,宛如一首空靈清麗的詩︰
山居秋暝‧王維
空山新雨後,
天氣晚來秋,
明月松間照,
清泉石上流;
竹喧歸浣女,
蓮動下漁舟,
隨意春芳歇,
王孫自可留。
有興趣者可以嘗試
SuperCollider tutorial
Also available as a downloadable zip of RTF, HTML and text files:
sctutorial.zip
Shortcuts:
1. Introduction and Overview
2. Sound Synthesis 1: Additive, Subtractive, Modulation
3. Sequencing
4. Interaction 1
5. Sound Synthesis 2: Sample-based, Granular
6. Effects
7. Interaction 2
8. Timing and Psychology of Rhythm
9. Algorithmic Composition
10. Open Sound Control, Server Messaging, Network Music
11. Sound Synthesis 3 – Physical Modelling
12. Sound Analysis
Extra exercises and SC technicalities: from arrays to classes
以及
Designing Sound in SuperCollider
This book is an independent project based on Designing Sound by Andy Farnell, all about the principles and techniques needed to design sound effects for real-time synthesis. The original book provides examples in the PureData language – here we have re-created some of the examples using SuperCollider.
The original book includes much more than what you see here – we’re only recreating the examples and not the text! So in a sense this is not a stand-alone book and you’ll get the most out of it if you have the original book with you. But we hope the examples are illustrative in themselves.
Any defects in the code we present should be assumed to be our own mistakes, and no reflection on Andy’s fine book!
,體驗將來國度也☆